The fast fashion industry, driven by rapid production and low costs, often overlooks the impact on local economies and communities. Slow fashion, a movement focusing on sustainability, quality, and ethical production, offers a promising alternative. By prioritizing local manufacturing, slow fashion empowers communities, creates jobs, and fosters a sense of cultural identity.
What is Slow Fashion?
Slow fashion promotes mindful consumption and values the craftsmanship behind every piece of clothing. Unlike fast fashion, which emphasizes speed and quantity, slow fashion focuses on:
- High-quality materials
- Ethical labor practices
- Reduced environmental impact
This shift benefits not just the environment but also local economies, particularly in areas rich in artisan traditions.

How Local Manufacturing Drives Economic Growth
Job Creation and Skill Development
Investing in local manufacturing creates stable employment opportunities. Workers learn valuable skills like tailoring, weaving, and dyeing, which are often passed down through generations.
- Example: Artisanal textile hubs in India and Peru support thousands of families through fair trade practices.

Boosting Small Businesses
Local slow fashion brands collaborate with small-scale workshops and independent artisans. This support strengthens micro-businesses and fosters entrepreneurship.
- Example: Ethical brands like People Tree and Christy Dawn work directly with local communities, ensuring fair wages and sustainable practices.
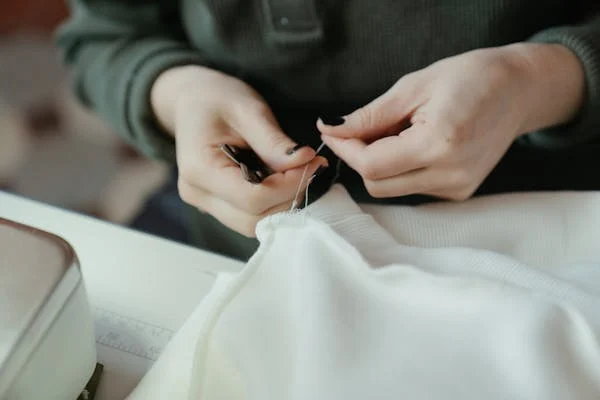

Preserving Cultural Heritage
Slow fashion often incorporates traditional techniques, keeping local artistry alive. By weaving cultural elements into modern designs, manufacturers celebrate and preserve heritage.
- Example: Indigenous weaving techniques from Guatemala are incorporated into global fashion collections.

Environmental Benefits of Local Slow Fashion
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Producing clothing locally minimizes transportation emissions. This is particularly impactful when compared to fast fashion, which relies on global supply chains.
Sustainable Resource Use
Local production often aligns with sustainable practices, such as using organic materials and minimizing waste.
Challenges of Local Manufacturing in Slow Fashion
Higher Production Costs
Local manufacturing can be more expensive than outsourcing. Slow fashion brands must balance affordability and fair wages.
Scaling Limitations
Producing on a smaller scale may not meet high demand, making it challenging for brands to grow without compromising their principles.
Consumer Perception
While awareness of slow fashion is growing, many consumers still prioritize affordability over sustainability.
Success Stories in Local Slow Fashion
Eileen Fisher
This brand supports local production by investing in renewable resources and circular fashion. Their repair and recycling programs have also set industry benchmarks. www.eileenfisher.com
Maiyet
Maiyet collaborates with artisans worldwide to bring traditional craftsmanship into contemporary fashion. Their efforts contribute directly to economic development. https://us.vestiairecollective.com/

Amour Vert
Focusing on “green love,” this U.S.-based brand emphasizes local manufacturing and low-impact materials to support sustainable production. www.amourvert.com

Steps to Support Local Economies Through Slow Fashion
For Brands:
- Source Locally: Use materials and talent from local suppliers to reduce outsourcing.
- Promote Artisan Work: Highlight traditional techniques and their significance in marketing campaigns.
- Adopt Transparent Practices: Showcase how investments directly benefit local communities.
For Consumers:
- Buy from Ethical Brands: Support companies committed to local manufacturing.
- Prioritize Quality Over Quantity: Choose timeless pieces that sustain the economy and reduce waste.
- Spread Awareness: Advocate for the benefits of slow fashion within your community.
The Broader Impact: A Ripple Effect
Slow fashion manufacturing extends benefits beyond individual communities. It contributes to:
- Economic stability in rural areas
- Global awareness of traditional craftsmanship
- A sustainable model for other industries
By aligning ethical principles with local economic development, slow fashion becomes more than a trend—it becomes a transformative movement for a greener and more equitable future.
Conclusion
Slow fashion manufacturing is a catalyst for positive change, blending sustainability with local economic empowerment. By embracing ethical practices, fostering cultural heritage, and creating opportunities for artisans, slow fashion offers a sustainable alternative to the fast fashion industry’s damaging impacts. Supporting this movement means choosing quality over quantity, advocating for fair labor practices, and celebrating the artistry of local communities. As both brands and consumers champion these values, slow fashion not only uplifts local economies but also sets a precedent for a more equitable and environmentally conscious global fashion industry.
About IGREEN TEX
IGREEN TEX is a provider of fashion and textile products, offering a wide range of apparel both domestically and internationally. Our commitment to quality ensures that our products not only meet the highest standards but also promote eco-friendly practices.
IGREEN TEX VIETNAM CO LTD
Address: No. 83, A4 Street, Ward 12, Tan Binh Dist, HCMC
Tax code: 0315844409
Email: info@igreentex.com
WhatsApp/Viber/Zalo: +84 938.045.900